The moon is the closest planet to the earth and the brightest and most easily observed object in the earth's night sky. Because the moon is always facing the same way towards the earth, for us humans living on earth, we can only ever observe one fixed side of the moon.
We usually refer to the side of the moon facing the earth as the front side of the moon and the other side as the back side of the moon, and by this definition, we on earth would never be able to see the back side of the moon. So the question arises, why does this happen? Is it a coincidence or is it something else?
It is true that there are many coincidences in the universe, and the emergence of our species, to say nothing of others, is in fact the result of the superposition of a large number of coincidences. However, the fact that the moon is always facing the same way towards the earth is not a coincidence, but rather a "Hidden agenda", although the so-called "Hidden agenda" Is not as mysterious as one might think. It is a phenomenon known as "Tidal locking", which we will learn more about below.

The first thing we need to understand is why the many planets in the universe are sphere-like in shape. Simply put, it is the effect of the planet's own gravity, which can be infinitely superimposed, so that when an object reaches a certain level of mass, its own gravity becomes so strong that the planet's matter as a whole behaves in a fluid-like state.
Ideally, when the matter of the planet reaches hydrostatic equilibrium, the planet would be a perfect sphere, but in reality this does not happen, because there are all sorts of factors in the universe that affect the shape of a planet, and the moon is certainly no exception.
As the moon revolves around the earth, it is affected by the earth's gravity, and on the other hand, due to its own inertia, it also has a tendency to move away from the centre of mass of the earth-moon system, which we can call the "Centrifugal force", in the opposite direction to the earth's gravity. This means that when the earth's gravity and the "Centrifugal force" Are in balance, the moon can steadily revolve around the earth.

(the "Centrifugal force" Is a virtual force introduced for the sake of discussion, but is actually a manifestation of the inertia of the object, so please be careful to distinguish between them)
Depending on the distance from the earth, there is a difference between the earth's gravitational force and the "Centrifugal force" On different parts of the moon, in that the closer the moon is to the earth, the greater the earth's gravitational force and the smaller the "Centrifugal force", and vice versa.
Because the moon is large enough, there is a significant difference between the earth's gravity and the 'centrifugal force' on parts of the moon that are farther apart, with the closest parts of the moon being subject to the greatest earth's gravity and the farthest parts of the moon being subject to the greatest 'centrifugal force'. The "Centrifugal force" Is greatest at the closest part of the moon to the earth.
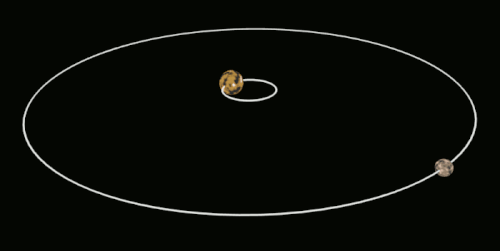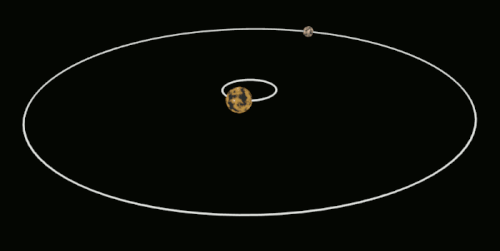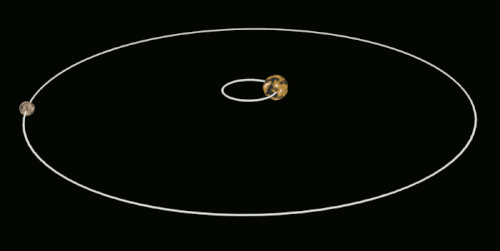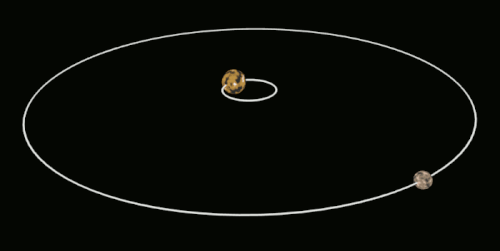
This affects the hydrostatic equilibrium of the moon and results in a slight bulge on both the "Front side" And the "Back side" Of the moon, also known as "Tidal bulge". This phenomenon is also known as "Tidal bulge" And can be simply interpreted as the moon's shape being pulled into an ellipsoid.
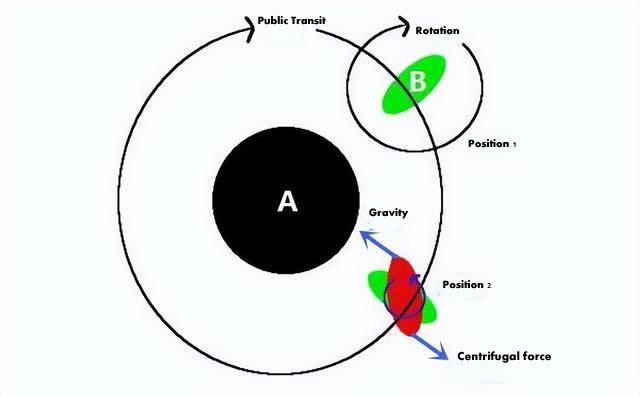
In the diagram above, a is the earth and b is the moon. When the moon is in position 1, it is pulled into an ellipsoid (which is not as dramatic as it could be).
As the 'tidal bulge' takes time to recover, there will be a pair of parallel forces of equal magnitude and opposite direction, but not in a straight line, at the two ends of the moon's 'tidal bulge' at position 1, one of which is the earth's gravitational force and the other is the 'centrifugal force'. The other is the 'centrifugal force', which can be thought of as a force couple.
As we all know, force couples can cause an object to rotate, so the moon will have a tendency to rotate in the opposite direction of its rotation, which will reduce the moon's original rotation speed. Conversely, if the moon's speed of rotation is slower than its speed of revolution, then the moon's speed of rotation will increase as it rotates to position 2.
As you can see, with the above mechanism, the moon's rotation and revolution will eventually be synchronised if time is long enough, meaning that for every revolution of the moon around the earth, it will complete exactly one rotation, a phenomenon known as 'tidal locking'.
According to scientists' estimates, the moon was born about 4.5 billion years ago, so we can imagine that even if its rotation and revolution were not synchronized at the beginning of its life, the moon would have been "Tidally locked" By the earth after such a long period of time, which is indeed the case.
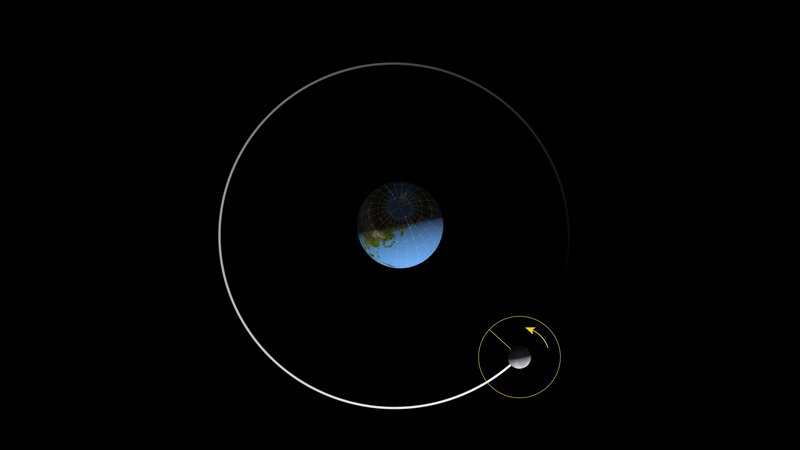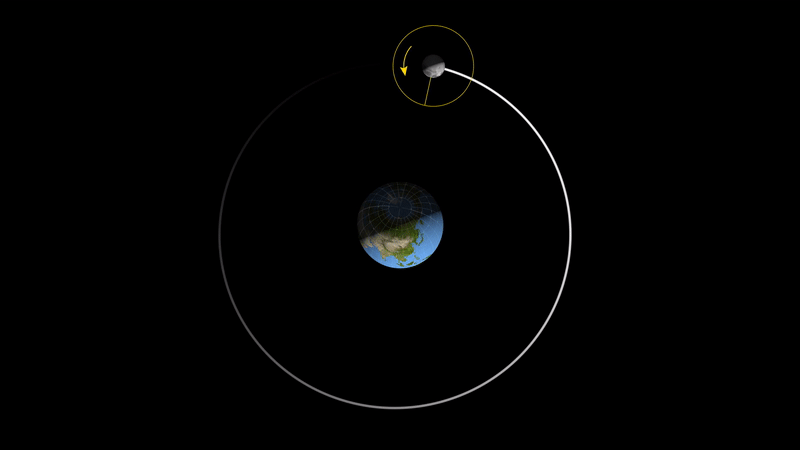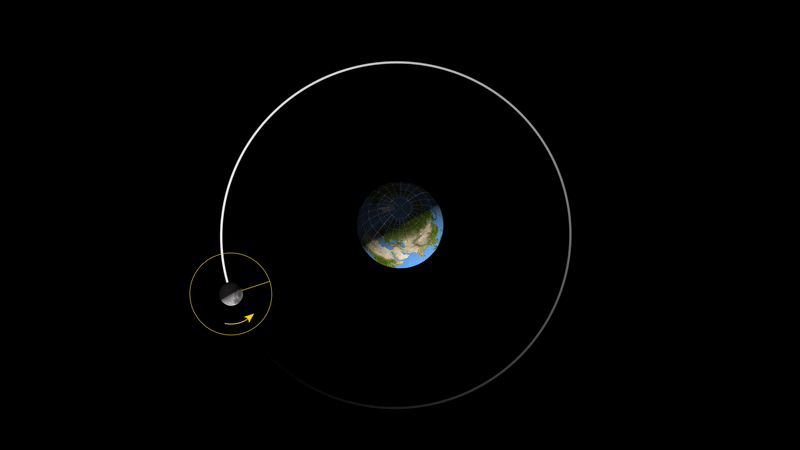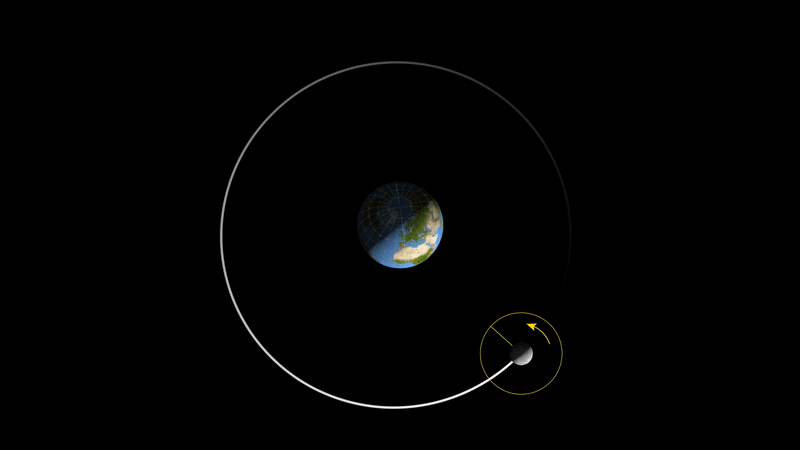
As shown above, the moon as we see it now actually rotates, but because its rotation period is exactly the same as its revolution period, the moon will always be facing the same way towards the earth, and we on earth will of course never see the back of the moon. This phenomenon is not a coincidence, but rather a result of the laws of the universe.
In fact, "Tidal locking" Is not uncommon in the universe, even in the solar system, where it is common for the moons of mars, jupiter, saturn, uranus, neptune and, most outrageously, pluto and its the most outrageous is pluto and its largest moon, cajun, as they are both tidally locked to each other.