As the tallest mountain on earth, the great name of mount everest can be said to be known to everyone on earth, but earth is not the only planet in the solar system with mountains, so are there mountains higher than everest on other planets in the solar system?

The answer is yes, for example, mount maxwell on venus. Mount maxwell is located in the northern hemisphere of venus (closer to the planet's north pole) and sounding data suggests that the mountain's highest peak is 10,943 metres above venus' datum, arguably higher than mount everest, yet mount maxwell is not considered the tallest in the solar system.
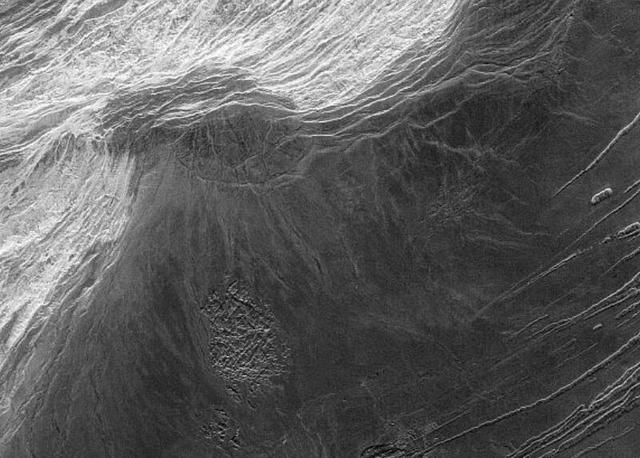
(↑mount maxwell)
Where is the tallest mountain in the solar system?
From the known soundings, the tallest mountain in the solar system is located on mars, and it is named mount olympus. This mountain is located in the northern hemisphere of mars (specifically at 18.65°, 226.2° e), and the soundings show that the highest peak of mount olympus is 21,171 m above the martian datum, far higher than mount everest on earth.
While we know that the himalayas, to which everest belongs, were formed by the collision of tectonic plates, olympus was not formed by the same mechanism, but simply by the gradual accumulation of magma that came out of the ground as it cooled.
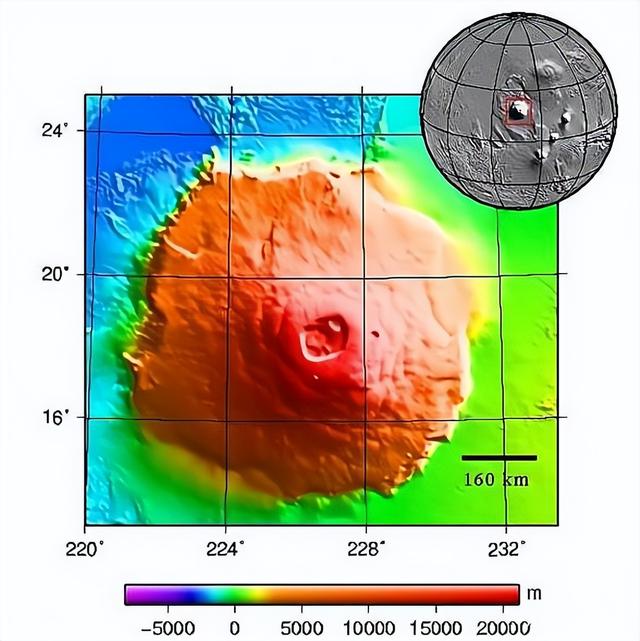
In fact, there are also 'shield volcanoes' on earth, the highest of which is mount mauna loa in the middle of the hawaiian islands, but this mountain is only 4,170 metres above sea level, and even from its base at sea level, its height from base to summit is only 10,203 metres, which is not even close to that of mount olympus. It is not comparable to mount olympus.
Why are the mountains on mars so much higher when they are also 'shield volcanoes'? The main reason is that the mass of mars is much smaller than that of earth, so the gravity of an object of the same mass on mars is much lower than on earth, and the low gravity environment allows the mountains on mars to "Grow" Taller and not be easily "Crushed" By gravity. "The low gravity environment would allow mountains on mars to 'grow' higher and not be easily 'crushed' by gravity.
What is the height of mount everest in the solar system?
If we restrict ourselves to the big planets in our solar system, everest would rank 7th in height, preceded in descending order by mount maxwell (which we have already mentioned), mount elysium (on mars, 14,127 metres), mount parmonis (on mars, about 15,000 metres), mount althea (on mars, 17,781 metres), mount aeschylus (on mars, 17,781 metres), and mount aeschylus. 17,781 m), mount aeschylus (located on mars at an altitude of 18,225 m), and mount olympus.
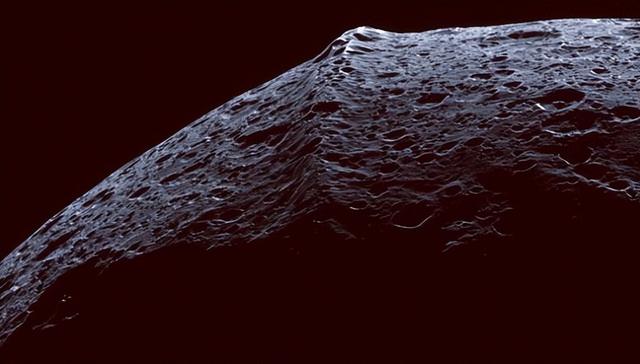
(↑ equatorial ridge on titan viii)
If we extend the range to smaller planets in the solar system, the ranking of mount everest moves back a little, for example the equatorial ridge on titan viii reaches a maximum of about 20,000 m, while mount boazoli on io is at least 16,000 m high.
In particular, the 'peak' in the central region of the rhea silveria basin on vesta can reach heights of 20 to 25 km (there is not enough data to give a range), so it is thought that this 'peak' is the tallest in the solar system, but since the height of this "Mountain" Is actually calculated from its base to its summit, so it is still commonly believed that olympus is the tallest mountain in the solar system, since the basin of rhea silvia is a crater and the height of this "Mountain" Is actually calculated from its base to its summit.
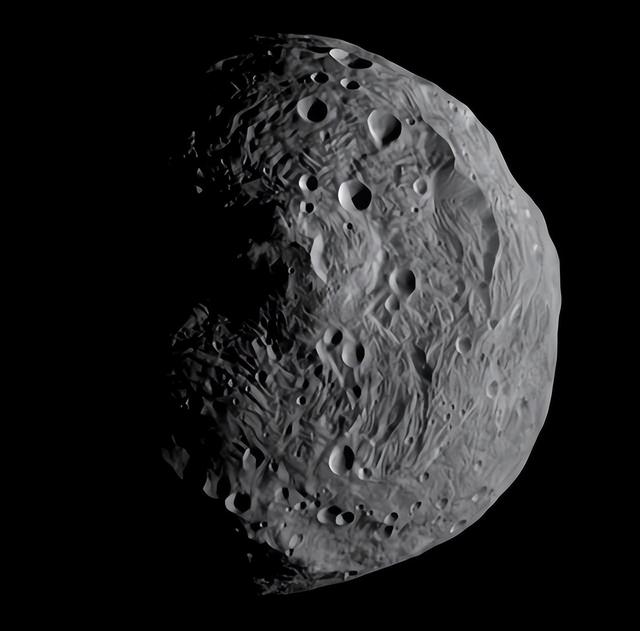

(↑ vesta)
Some people may say that the height of mount everest actually refers to its height above the sea level of the earth, whereas there are no oceans on other planets, and certainly no such thing as sea level, so such a ranking is actually unfair to mount everest.
To be fair, let's take another look at how high everest would be if all of the earth's oceans were removed.
When describing the height of an object, we need a datum to define 'height to zero', and on earth, mean sea level is a natural datum, whereas for a planet without liquid oceans, we need to define a datum in some other way.
How is it defined? A common method is to use a model of the planet's gravity field to calculate a gravitational equivalence plane that is closest to the average height of the planet's surface and use this as a datum to describe the height of objects on the surface of the planet.
On earth, we refer to the gravitational equilibrium that coincides with the surface of the resting ocean as the "Geoid", which is the equivalent of what is often referred to as sea level.
The volume of the earth's oceans is known to be about 1.37 billion cubic kilometres, and the surface area of the earth is about 510 million square kilometres. A simple calculation shows that if the earth's oceans were spread evenly over the surface of the earth, their depth would be about 2,686 metres. 11534m.

As can be seen, even if all of the earth's oceans were removed, everest would only rank above mount maxwell on venus in the solar system, and its height would still be far below that of the tallest mountain in the solar system.